How to use the DEC2HEX function
What is the DEC2HEX function?
The DEC2HEX function converts a decimal number to a hexadecimal number.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
What is a decimal number?
The decimal system is a positional numeral system that uses 10 as the base, it requires 10 different numerals: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. The dot or the decimal point represents decimal fractions which are not whole numbers.
The decimal number 520 has three positions, each with a different weight. It starts with 10^0 on the right and increases by one power on each additional position to the left.
520 = (5*10^2)+(2*10^1)+(0*10^0)
520 = 500 + 20 + 0
What is a hexadecimal number?
A hexadecimal number is a number with a base of 16, for example, the decimal system uses a base of 10. This means that each digit in a hexadecimal number can have 16 possible values, from 0 to 15, however, the letters A to F are used from 10 to 15. See the hexadecimal column in the table below.
Hexadecimal numbers are often used in computers, the reason is they represent four binary digits (bits) with one hexadecimal digit. For example, the binary number 1010 is equivalent to the hexadecimal number A.
Hexadecimals make it easier to write big numbers with less digits, in other words, hexadecimals shorten binary digits considerably. For example, we can use hexadecimal to show the values of colors and MAC addresses in computers.
The following table shows the binary, decimal and hexadecimal values from 0 (zero) to 17.
| Decimal | Hexadecimal |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 |
| 6 | 6 |
| 7 | 7 |
| 8 | 8 |
| 9 | 9 |
| 10 | A |
| 11 | B |
| 12 | C |
| 13 | D |
| 14 | E |
| 15 | F |
| 16 | 10 |
| 17 | 11 |
2. Syntax
DEC2HEX(number, [places])
3. Arguments
| number | Required. The decimal integer you want to convert. |
| [places] | Optional. The number of characters to use. If not entered the function uses the number of characters needed to complete the task. This argument allows you to add leading 0s (zeros). |
4. Example
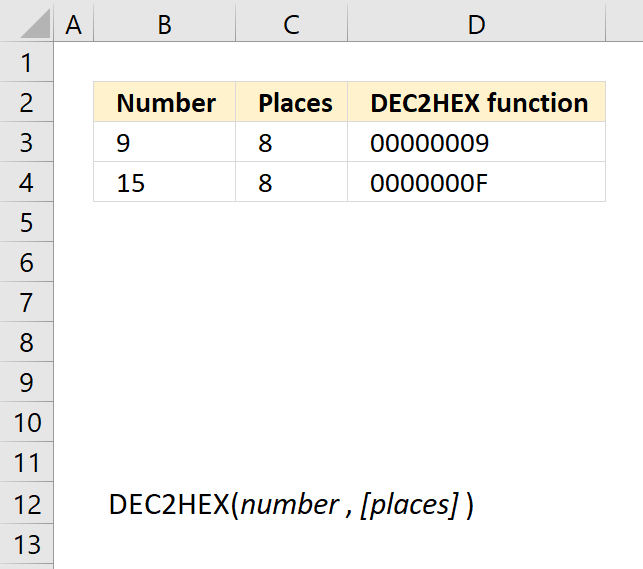
The image above shows the DEC2HEX function in cells D3 an D4. It calculates the hexadecimal values based on the corresponding cells which contain different decimal numbers and [places].
Formula in cell D3:
The first cell B3 contains 9 and cell C3 contains the places number, the DEC2HEX function returns 00000009 in cell D3, the second cell B4 contains 15 and the DEC2HEX function returns 0000000F in cell D4.
The next section describes how these values are calculated in detail.
5. How is the function calculated in detail?
There are different methods converting between decimal and hexadecimal, here is one way. Follow these steps to convert from decimal to hexadecimal:
- Divide the decimal number by 16 and write down the quotient and the remainder.
- Repeat the process with the quotient until it is zero. Make sure to note each quotient and remainder as you calculate each number.
- The hexadecimal number is the remainders from bottom to top.
For example, let us convert decimal number 199 to hexadecimal.
199/16 = 12 and remainder 7
12/16 = 0 and remainder 12 (B)
Decimal value 12 is hexadecimal value "B", see the conversion table above. The hexadecimal number is formed from the remainders counting from bottom to top. 199 = B7
6. Function not working
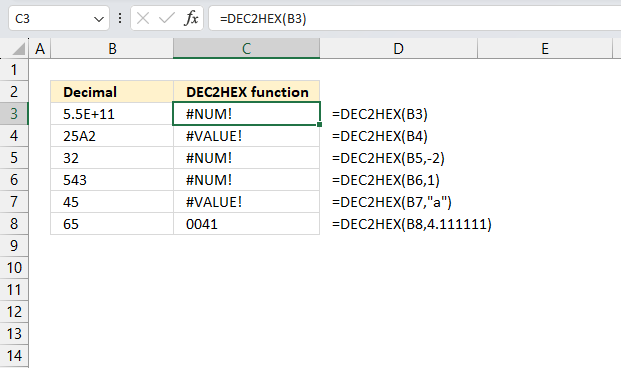
DEC2HEX returns the #NUM! error value if
- Number is less than -549,755,813,888 or larger than 549,755,813,887. See cells B3 and C3 in the image above.
- [places] is negative. See the formula next to cell C5.
- it requires more than the specified places characters. See the formula next to cell C6.
DEC2HEX returns the #VALUE! error if
- [places] is not a number. See the formula next to cell C7.
- The number is not a valid base 10 number. See cells B4 and C4 in the image above.
The second argument [places]is truncated if it is not an integer. For example, [places] is 4.1111111111 and the DEC2HEX function truncates it to 4. See the formula next to cell C8.
DEC2HEX ignores places and returns a 10-character hexadecimal number if the decimal number is negative.
6.1 Troubleshooting the error value
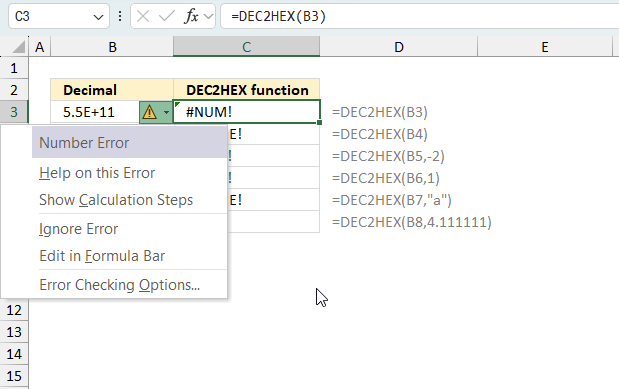
When you encounter an error value in a cell a warning symbol appears, displayed in the image above. Press with mouse on it to see a pop-up menu that lets you get more information about the error.
- The first line describes the error if you press with left mouse button on it.
- The second line opens a pane that explains the error in greater detail.
- The third line takes you to the "Evaluate Formula" tool, a dialog box appears allowing you to examine the formula in greater detail.
- This line lets you ignore the error value meaning the warning icon disappears, however, the error is still in the cell.
- The fifth line lets you edit the formula in the Formula bar.
- The sixth line opens the Excel settings so you can adjust the Error Checking Options.
Here are a few of the most common Excel errors you may encounter.
#NULL error - This error occurs most often if you by mistake use a space character in a formula where it shouldn't be. Excel interprets a space character as an intersection operator. If the ranges don't intersect an #NULL error is returned. The #NULL! error occurs when a formula attempts to calculate the intersection of two ranges that do not actually intersect. This can happen when the wrong range operator is used in the formula, or when the intersection operator (represented by a space character) is used between two ranges that do not overlap. To fix this error double check that the ranges referenced in the formula that use the intersection operator actually have cells in common.
#SPILL error - The #SPILL! error occurs only in version Excel 365 and is caused by a dynamic array being to large, meaning there are cells below and/or to the right that are not empty. This prevents the dynamic array formula expanding into new empty cells.
#DIV/0 error - This error happens if you try to divide a number by 0 (zero) or a value that equates to zero which is not possible mathematically.
#VALUE error - The #VALUE error occurs when a formula has a value that is of the wrong data type. Such as text where a number is expected or when dates are evaluated as text.
#REF error - The #REF error happens when a cell reference is invalid. This can happen if a cell is deleted that is referenced by a formula.
#NAME error - The #NAME error happens if you misspelled a function or a named range.
#NUM error - The #NUM error shows up when you try to use invalid numeric values in formulas, like square root of a negative number.
#N/A error - The #N/A error happens when a value is not available for a formula or found in a given cell range, for example in the VLOOKUP or MATCH functions.
#GETTING_DATA error - The #GETTING_DATA error shows while external sources are loading, this can indicate a delay in fetching the data or that the external source is unavailable right now.
6.2 The formula returns an unexpected value
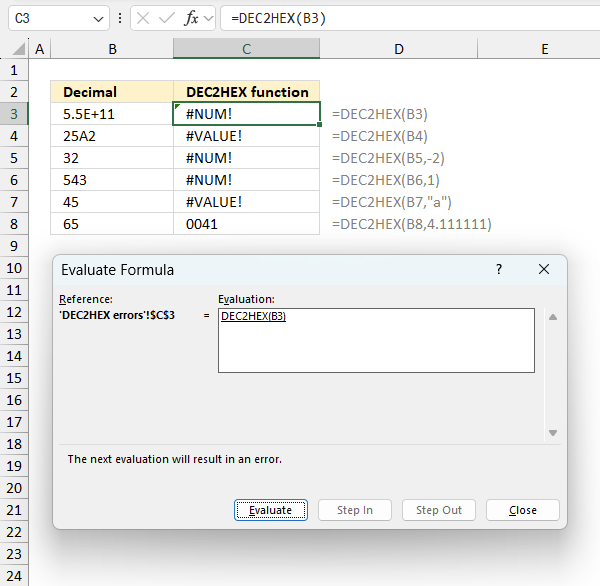
To understand why a formula returns an unexpected value we need to examine the calculations steps in detail. Luckily, Excel has a tool that is really handy in these situations. Here is how to troubleshoot a formula:
- Select the cell containing the formula you want to examine in detail.
- Go to tab “Formulas” on the ribbon.
- Press with left mouse button on "Evaluate Formula" button. A dialog box appears.
The formula appears in a white field inside the dialog box. Underlined expressions are calculations being processed in the next step. The italicized expression is the most recent result. The buttons at the bottom of the dialog box allows you to evaluate the formula in smaller calculations which you control. - Press with left mouse button on the "Evaluate" button located at the bottom of the dialog box to process the underlined expression.
- Repeat pressing the "Evaluate" button until you have seen all calculations step by step. This allows you to examine the formula in greater detail and hopefully find the culprit.
- Press "Close" button to dismiss the dialog box.
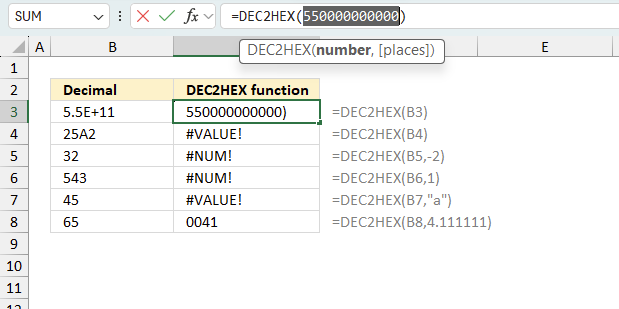
There is also another way to debug formulas using the function key F9. F9 is especially useful if you have a feeling that a specific part of the formula is the issue, this makes it faster than the "Evaluate Formula" tool since you don't need to go through all calculations to find the issue..
- Enter Edit mode: Double-press with left mouse button on the cell or press F2 to enter Edit mode for the formula.
- Select part of the formula: Highlight the specific part of the formula you want to evaluate. You can select and evaluate any part of the formula that could work as a standalone formula.
- Press F9: This will calculate and display the result of just that selected portion.
- Evaluate step-by-step: You can select and evaluate different parts of the formula to see intermediate results.
- Check for errors: This allows you to pinpoint which part of a complex formula may be causing an error.
The image above shows cell reference B3 converted to hard-coded value using the F9 key. The DEC2HEX function requires valid numerical values which is not the case in this example. We have found what is wrong with the formula.
Tips!
- View actual values: Selecting a cell reference and pressing F9 will show the actual values in those cells.
- Exit safely: Press Esc to exit Edit mode without changing the formula. Don't press Enter, as that would replace the formula part with the calculated value.
- Full recalculation: Pressing F9 outside of Edit mode will recalculate all formulas in the workbook.
Remember to be careful not to accidentally overwrite parts of your formula when using F9. Always exit with Esc rather than Enter to preserve the original formula. However, if you make a mistake overwriting the formula it is not the end of the world. You can “undo” the action by pressing keyboard shortcut keys CTRL + z or pressing the “Undo” button
6.3 Other errors
Floating-point arithmetic may give inaccurate results in Excel - Article
Floating-point errors are usually very small, often beyond the 15th decimal place, and in most cases don't affect calculations significantly.
Useful resources
DEC2HEX function - Microsoft
Decimal to Hexadecimal converter
How to convert decimal to hexadecimal
'' function examples
Table of Contents How to use the DEC2BIN function How to use the DEC2HEX function How to use the DEC2OCT […]
What's on this page Reverse text Insert random characters Convert letters to numbers How to shuffle characters in the alphabet […]
Functions in 'Engineering' category
The DEC2HEX function function is one of 42 functions in the 'Engineering' category.
How to comment
How to add a formula to your comment
<code>Insert your formula here.</code>
Convert less than and larger than signs
Use html character entities instead of less than and larger than signs.
< becomes < and > becomes >
How to add VBA code to your comment
[vb 1="vbnet" language=","]
Put your VBA code here.
[/vb]
How to add a picture to your comment:
Upload picture to postimage.org or imgur
Paste image link to your comment.
Contact Oscar
You can contact me through this contact form