Run a macro every time a workbook opens or closes
This article explains how to set up a workbook so a macro is run every time you open the workbook. Excel Event code makes this possible and it is easier than you think.
Event code can run a macro based on a drop-down list, event code is VBA code stored in a worksheet module or workbook module. I will explain this later on in this article.
For example, you could have a macro that opens another workbook that you need which automates this task, saving you time, making you happy, and feeling awesome.
What's on this page
- Introduction
- Run a macro automatically when a specific workbook is opened
- Run a macro automatically when selecting a specific worksheet
- Run macro when a specific cell is selected
- Get Excel *.xlsm file
- Select cell A1 on all sheets before you close a workbook - VBA
- How to log when a workbook is opened and closed - VBA
1. Introduction
What is VBA?
VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a programming language developed by Microsoft that is used for automating tasks in Microsoft Office applications such as Excel, Word, and Access. It allows users to create macros, automate repetitive tasks, and enhance Office functionality with custom scripts.
What is a macro?
In Microsoft Excel, a macro is a sequence of instructions written in Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) that allows you to automate repetitive tasks time consuming tedious tasks. Macros can perform a wide range of actions from simple formatting changes to complex data manipulations.
What is an event?
An event in Excel refers to an action or occurrence that triggers the execution of a specific macro. Events can be user-initiated, such as opening a workbook, changing a cell's value, or press with left mouse button oning a button, or system-initiated, like recalculating a worksheet. By associating macros with events users can automate responses to specific actions within the workbook.
What is event code?
Event code is placed in specific object modules like ThisWorkbook or a worksheet module (Sheet1, Sheet2). Regular VBA code is typically stored in a standard VBA module like Module1, Module2, etc...
What is an *.xlsm file?
Older Excel versions saved Excel files using the *.xls as the file extension. It was also possible to save VBA code in an *.xls file which made them potentially unsafe.
Excel 2007 introduced *.xlsx and *.xlsm files which made it safer to use Excel files. An *.xlsx file cant contain VBA code at all making them safer to use in contrast to older *.xls files
An .xlsm file is a type of Excel workbook that also supports macros which are automated scripts written in VBA which *.xlsx don't do. They use the Open XML format and differ from standard .xlsx files because they can store and run macros. This feature extends the capabilities of worksheets allowing you to automate processes and improve spreadsheet functionality. It's important to exercise caution when handling .xlsm files from untrusted sources as macros can contain code that may pose security risks.
1. Run a macro automatically when a specific workbook is opened
You will now learn to:
- Create a macro that opens a specific workbook.
- Where to put the VBA code.
- How to run the macro.
- Where to put event code.
Remember to save the workbook as a *.xlsm file to make sure the VBA code stays attached.
1.1 Create a macro
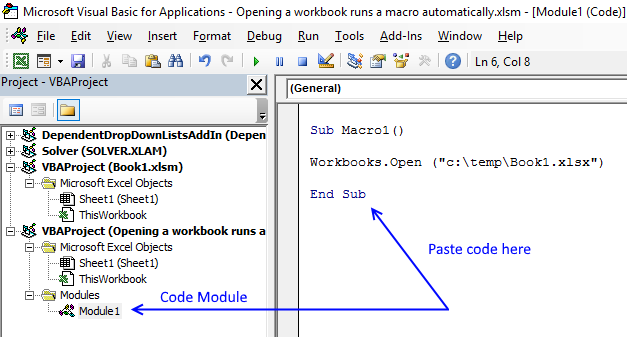
The following macro opens workbook Book1.xlsx in folder c:\temp
'Name macro
Sub Macro1
'Open a given workbook
Workbooks.Open ("c:\temp\Book1.xlsx")
End Sub
1.2 Where to put the code?
Copy the macro code above and go to tab "Developer" on the ribbon. If it is missing search the internet for your Excel version and "Show developer tab".
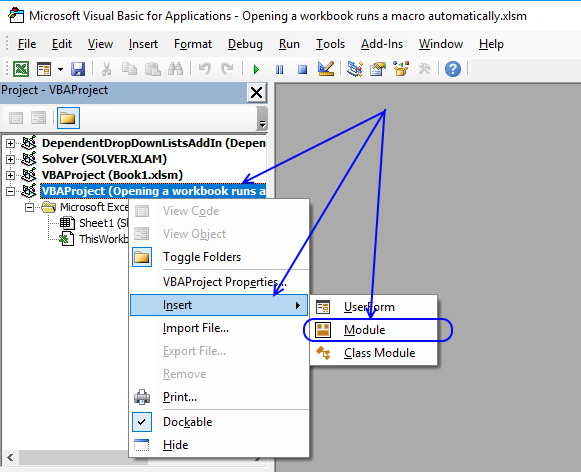
Press with mouse on "Visual Basic" button to open the Visual Basic editor. Press with right mouse button on on your workbook in the Project Explorer window.
Press with mouse on "Insert" and then on "Module". This action adds a code module to your workbook.
Now paste the VBA code above to your code module.
Go back to Excel.
1.3 How to run macro
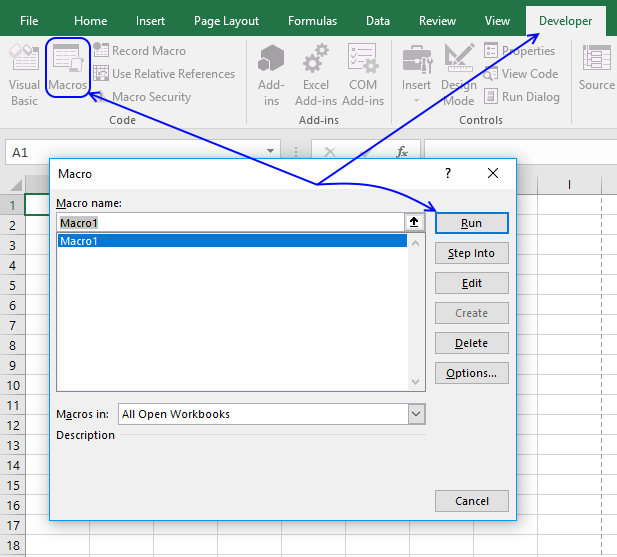
Go to tab "Developer" and press with left mouse button on the "Macro" button. The following dialog box appears:
Press with mouse on "Run" button and the workbook is opened.
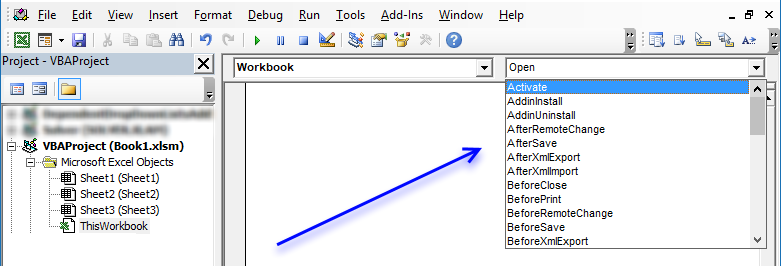
1.4 Where to put event code?
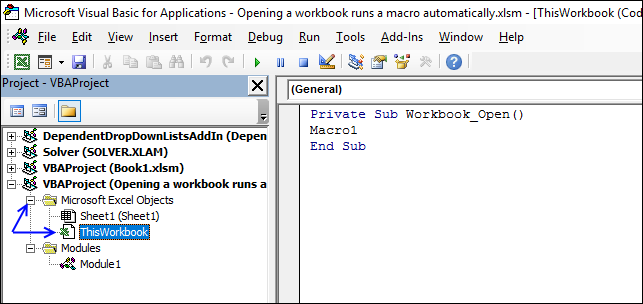
Press Alt+F11 to open the VB Editor or go to tab "Developer" on the ribbon, press with left mouse button on "Visual Basic" button. Double press with left mouse button on "This Workbook", if you can't see it expand the list by press with left mouse button oning on the + sign.
Paste the following event code to the workbook module:
Private Sub Workbook_Open() Macro1 End Sub
Go back to Excel. Save the workbook with file extension *.xlsm, this is important.
Close workbook and open it again. The workbook Book1.xlsx in folder c:\temp is now automatically opened. (If it exists..)
2. Run a macro automatically when selecting a specific worksheet
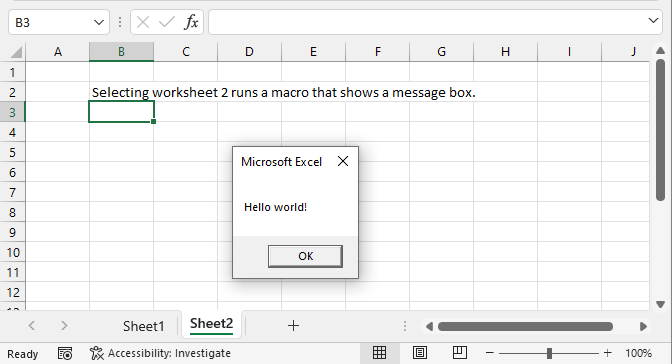
This section describes how to run a macro if a specific worksheet is selected (activated). Each worksheet in a workbook has a corresponding worksheet module that you can easily access, however, put only event code in these modules.
Note, put regular macros in regular modules.
2.1 Worksheet event code
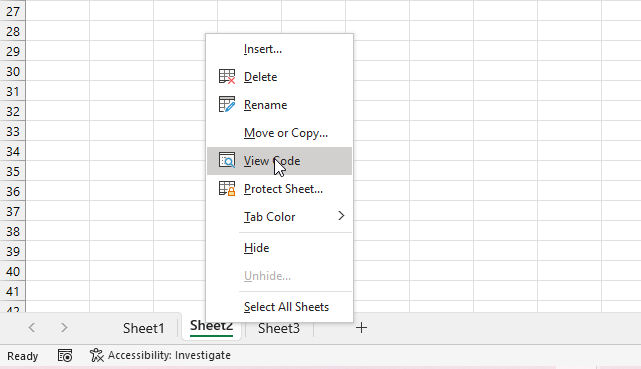
The following steps describe how to save event code to a specific worksheet.
- Press the right mouse button on the worksheet tab you want to edit, it is located at the left bottom of your Excel window.
- A pop-up menu appears, see the image above.
- Press with the left mouse button on "View Code" to open the corresponding worksheet module in Visual Basic Editor (VBE).
- Copy event code below.
- Paste to worksheet module.
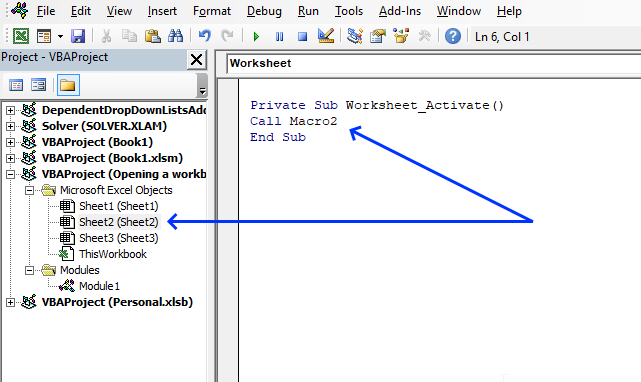
'Event code that runs when the user press with left mouse button ons on a specific worksheet tab Private Sub Worksheet_Activate() 'Start macro named Macro2 Call Macro2 End Sub
2.2 Macro code

The following VBA code is a regular macro. it shows a message box containing "Hello world!". Here is how you store regular macros:
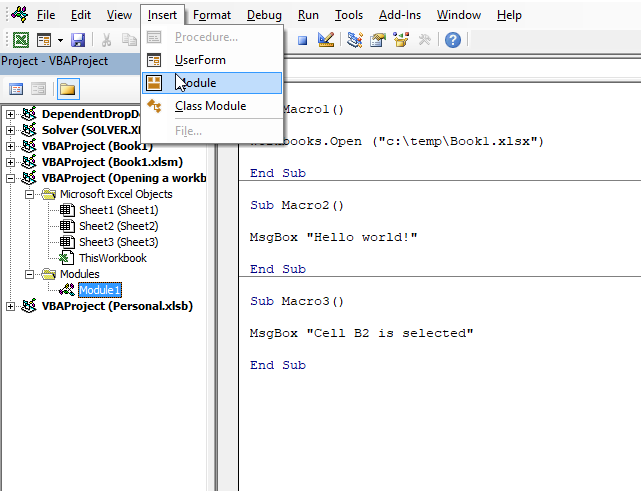
- Press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor.
- Press the left mouse button on "Insert" on the top menu, see the image below.
- Press the left mouse button on "Module" to create a new module, they are located in the Modules folder shown in the image below.
- Copy code below.
- Paste to the module.
- Exit Visual Basic Editor.
Sub Macro2() MsgBox "Hello world!" End Sub
3. Run macro when a specific cell is selected
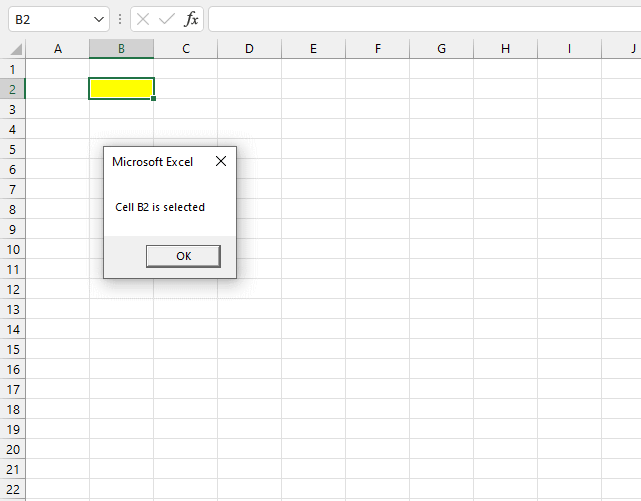
The image above demonstrates a macro that is run when a specific cell is selected on a specific worksheet. The example shown in the image above shows a message box containing text "Cell B2 is selected" when cell B2 is selected.
3.1 Worksheet code
The following steps describe how to save event code to a specific worksheet.
- Press the right mouse button on the worksheet tab you want to edit, it is located at the left bottom of your Excel window.
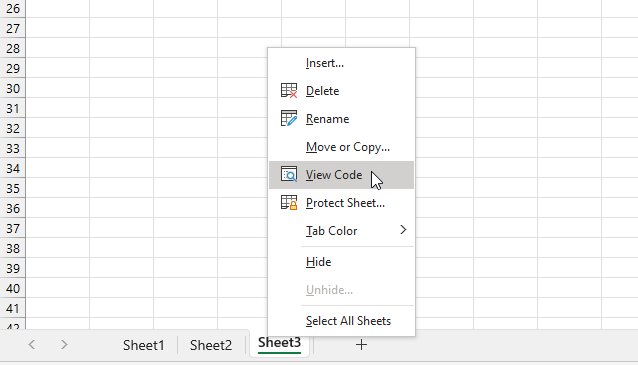
- A pop-up menu appears, see the image above.
- Press with the left mouse button on "View Code" to open the corresponding worksheet module in Visual Basic Editor (VBE).
- Copy event code below.
- Paste to worksheet module.
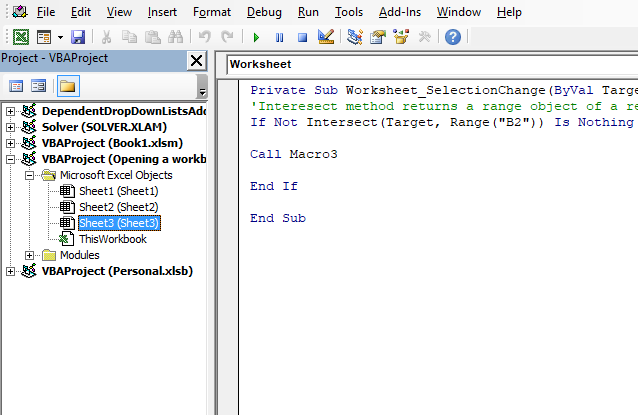
'Event code
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
'Interesect method returns a range object of a rectangular intersection of two or more cell ranges
If Not Intersect(Target, Range("B2")) Is Nothing Then
'Start macro named Macro3
Call Macro3
End If
End Sub
3.2 Macro code

The following VBA code is a regular macro. it shows a message box containing "Cell B2 is selected". Here is how you store regular macros:
- Press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor.
- Press the left mouse button on "Insert" on the top menu, see the image below.
- Press the left mouse button on "Module" to create a new module, they are located in the Modules folder shown in the image below.
- Copy code below.
- Paste to the module.
- Exit Visual Basic Editor.

Sub Macro3() MsgBox "Cell B2 is selected" End Sub
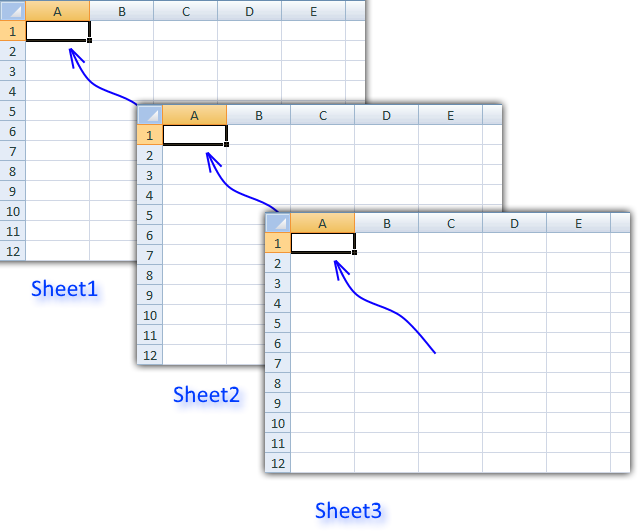
5. Select cell A1 on all sheets before you close a workbook - VBA
This post demonstrates a macro that automatically selects cell A1 on each sheet right before you close a workbook. The VBA code also moves the view so cell A1 is the upper left cell on all sheets.
This macro is different from regular macros, it is rund when something happens, Microsoft calls this an Event. An event macro has a designated name and must be placed in the sheet module or worksheet module. If your event code is not working you probably saved the code in a regular module.
You can see a list of available events in the workbook or sheet module.
The following code selects cell A1 in all visible sheets right before you close the workbook. You can save this macro in a regular module as well, however, you then need to run the macro manually.
VBA code
'This Event macro fires before you close a workbook and before the user is prompted to save changes.
Private Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean)
'Declare variables and data types
Dim sht As Worksheet, csheet As Worksheet
'Don't show any changes the macro does on the screen, this will also make the macro faster.
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
'Assigns object active sheet to variable csheet so we can go back to this sheet when the macro is finished.
Set csheet = ActiveSheet
'Iterate through each worksheet in active workbook
For Each sht In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
'Check if worksheet is not hidden
If sht.Visible Then
'Activate sheet
sht.Activate
'Select cell A1 in active worksheet
Range("A1").Select
'Zoom to first cell
ActiveWindow.ScrollRow = 1
ActiveWindow.ScrollColumn = 1
End If
'Contine with remaining worksheets
Next sht
'Go back to the worksheet when this event started
csheet.Activate
'Show all changes made to the workbook
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
Where to copy the code
- Press Alt-F11 to open Visual Basic Editor
- Double press with left mouse button on ThisWorkbook in Project Explorer.
Ctrl + R opens Project Explorer.
- Copy aboveVBAa code.
- Paste to worksheet module.
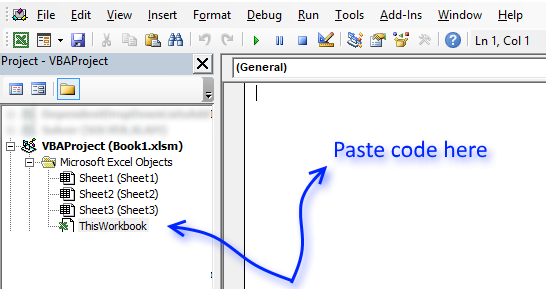
- Exit visual basic editor
Recommended article
Recommended articles
Save links to your favorite macros in a personal tab on the ribbon for easy access and to become more […]
6. How to log when a workbook is opened and closed - VBA
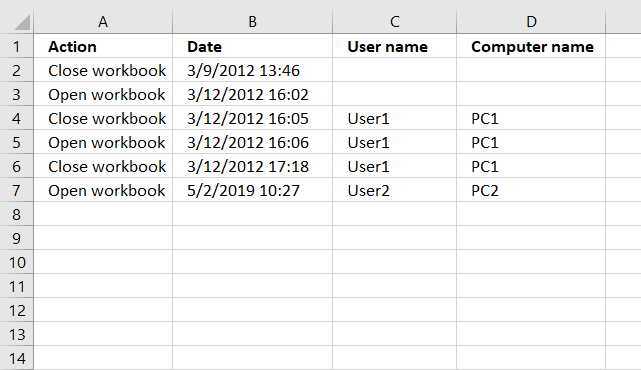
This article demonstrates how to automatically create log entries when a workbook opens or closes using event code. Column A contains the action, Open or Close, column B contains the date and time.
Column C contains the user name and column D contains the computer name. Do not paste the code below to a regular module, that won't work. There are detailed instructions below.
6.1 VBA code
'This event code begins right before the user closes the workbook.
Private Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean)
'Dimension variable and declare data type
Dim Lrow As Single
'Save the row of the first empty cell in column A to variable Lrow.
Lrow = Worksheets("Log").Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row + 1
'Check if cell above equals text value "Close Workbook",
'if true then withdraw value in Lrow with 1 and then save the result to Lrow
If Worksheets("Log").Range("A" & Lrow - 1).Value = "Close workbook" Then Lrow = Lrow - 1
'Save text value "Close Workbook" to cell
Worksheets("Log").Range("A" & Lrow).Value = "Close workbook"
'Save date and time to the corresponding cell in column B.
Worksheets("Log").Range("B" & Lrow).Value = Now
End Sub
6.2 Where to copy code?
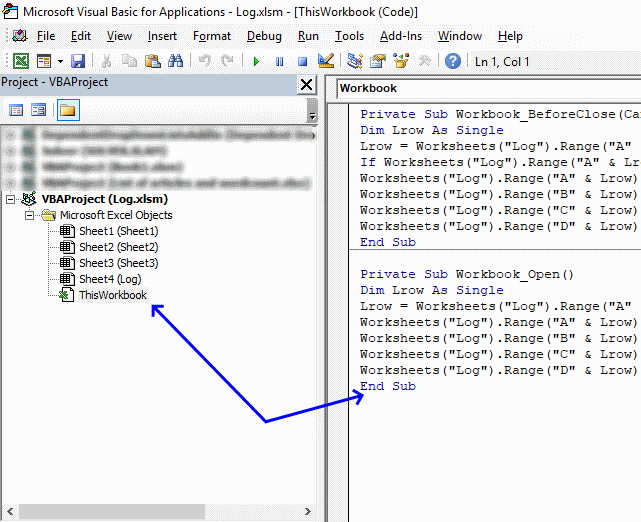
- Go to tab "Developer" on the ribbon and press with left mouse button on "Visual Basic" button to open the Visual Basic Editor or press shortcut keys Alt+F11
- Double press with left mouse button on "This workbook" in the project explorer.
- Paste code to workbook module.
- Return to Excel.
- Save your workbook as an *.xslm file in order to save the code as well.
'This event code starts when the workbook is opened.
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
'Dimension variable and declare data type
Dim Lrow As Single
'Save the row of the first empty cell in column A to variable Lrow.
Lrow = Worksheets("Log").Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row + 1
'Save text value "Open Workbook" to the first empty cell
Worksheets("Log").Range("A" & Lrow).Value = "Open workbook"
Save date and time to the corresponding cell in column B.
Worksheets("Log").Range("B" & Lrow).Value = Now
End Sub
Macro category
Table of Contents How to create an interactive Excel chart How to filter chart data How to build an interactive […]
Table of Contents Excel monthly calendar - VBA Calendar Drop down lists Headers Calculating dates (formula) Conditional formatting Today Dates […]
Table of Contents Split data across multiple sheets - VBA Add values to worksheets based on a condition - VBA […]
Excel categories
13 Responses to “Run a macro every time a workbook opens or closes”
Leave a Reply
How to comment
How to add a formula to your comment
<code>Insert your formula here.</code>
Convert less than and larger than signs
Use html character entities instead of less than and larger than signs.
< becomes < and > becomes >
How to add VBA code to your comment
[vb 1="vbnet" language=","]
Put your VBA code here.
[/vb]
How to add a picture to your comment:
Upload picture to postimage.org or imgur
Paste image link to your comment.
Hi Oscar,
Is there a way to include the name of the person (from computer name or user name, which appears in the excel options)in the code?
This would be a nice option to have when there are multiple users.
Regards,
Nilhan
Nilhan,
Sure!
Private Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean) Dim Lrow As Single Lrow = Worksheets("Log").Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row + 1 If Worksheets("Log").Range("A" & Lrow - 1).Value = "Close workbook" Then Lrow = Lrow - 1 Worksheets("Log").Range("A" & Lrow).Value = "Close workbook" Worksheets("Log").Range("B" & Lrow).Value = Now Worksheets("Log").Range("C" & Lrow).Value = Environ("USERNAME") Worksheets("Log").Range("D" & Lrow).Value = Environ("COMPUTERNAME") End Sub Private Sub Workbook_Open() Dim Lrow As Single Lrow = Worksheets("Log").Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row + 1 Worksheets("Log").Range("A" & Lrow).Value = "Open workbook" Worksheets("Log").Range("B" & Lrow).Value = Now Worksheets("Log").Range("C" & Lrow).Value = Environ("USERNAME") Worksheets("Log").Range("D" & Lrow).Value = Environ("COMPUTERNAME") End SubHello Oscar, is it possible to put this VBA code into a spreadsheet and then get the results to appear along with the file name on a different spreadsheet?
Many thanks
Dale
Hi Oscar not sure if you answered Dale's question but wondering if the results can appear in a separate file
thanks... works great!
I'm using Excel 2010, but it doesn't work on my computer.
Something changed in Excel?
Oct 2021
Working OK on Office 365.
Thanks
Thanks a lot, very helpful I took the code further by inserting same data on all selected cell, thanks again saved a lot of time
Hi, For this to save in the A1 position so it opens in this same way do I need to add ActiveWorkbook.Save?
I should note I was trying to do this in the Personal notebook in "ThisWorksheet" so that it would happen for every document I close. Is this possible?
Hi Oscar and Sevgili Nilhan,
Both of your question and answer did alot for me, thank you very much.
Regards
Working great for my requirement... Thank you so much
sharanesh,
you are welcome!