Calculate machine utilization
This article explains how to calculate an overlapping time ranges across multiple days. This can be very useful in situations like:
- Accurately calculating usage of equipment, vehicles, machines etc.
- Determining how much to bill a client when a service is provided.
- Calculating energy consumption based on usage time.
- Measuring employee hours worked.
The first example (section 1) shows how to calculate total time based on a time interval repeated daily. The second example (section 2) shows how to calculate the total time based on time intervals specified on weekdays repeated weekly.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
What is an Excel date?
An Excel date is a numeric value representing a specific calendar day. Excel stores dates as serial numbers, where January 1, 1900 is 1, January 2, 1900 is 2, and so on. This allows for easy calculations involving dates.
What is Excel time?
An Excel time is a fractional value representing a specific time within a day. It is stored as a decimal between 0 and 1, where:
- 0.00 = 12:00 AM (midnight)
- 0.50 = 12:00 PM (noon)
- 0.75 = 6:00 PM
Times are fractions of a full day, so 6 hours = 0.25 (¼ of a day).
What is overlapping date and time ranges?
Overlapping date and time ranges occur when two periods partially or fully intersect. For example:
- Range 1: March 1, 10:00 AM – March 1, 4:00 PM
- Range 2: March 1, 2:00 PM – March 1, 6:00 PM
Since both ranges cover 2:00 PM to 4:00 PM, they overlap. Overlapping occurs when the start of one range is before the end of another, and vice versa.
2. Calculate total time based on a time range across multiple days

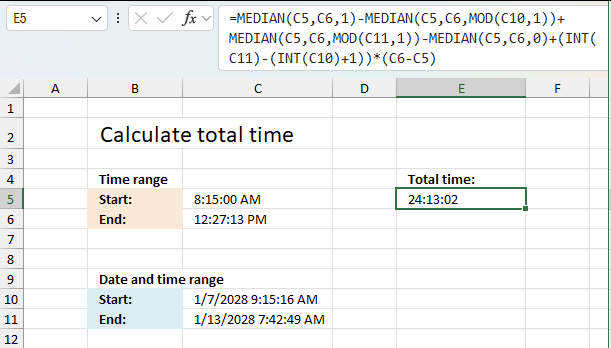
This example demonstrates a formula that calculates the total time based on a time range that repeats ever day. The start time is 8:15:00 PM and is displayed in cell C5. The end time is 12:27:13 PM which is shown in cell C6. This time range repeats everyday. Note that the time range contains hours, minutes, and seconds.
The question is what is the total time if the range is between
- 1/7/2028 9:15:16 AM
- 1/13/2028 7:42:49 AM.
The following formula calculates the total time based on these conditions:
There are three different calculations in this formula:
- The overlapping time for the start date (1/7/2028) only.
- MEDIAN(C5,C6,1)-MEDIAN(C5,C6,MOD(C10,1))
- The overlapping time for the end date only (1/13/2028).
- MEDIAN(C5,C6,MOD(C11,1))-MEDIAN(C5,C6,0)
- Total time based on days between the start date and end date excluding the start and end date.
- (INT(C11)-(INT(C10)+1))*(C6-C5)
What is time in Excel? Excel time value is a number equal to or larger than 0 (zero) and smaller than or equal to 1, formatted as a time value. One hour is 1/24, there are 24 hours in one day. One minute is 1/1440, there are 1440 minutes in one day (60*24 = 1440). One second is 1/86400, there are 86400 seconds in one day (60*60*24 = 86400).
The following table shows whole hours, one hour is 1/24, 2 hours is 2/24, and so on.
0 - 12:00:00 AM
1/24 - 1:00:00 AM
2/24 - 2:00:00 AM
...
23/24 - 11:00:00 PM
24/24 - 12:00:00 AM
The time value is only the decimal part of a number, in other words, a value larger than or equal to 1 makes no difference, Excel uses only the decimal part of a number to create an Excel time value. 1.5 -> 0.5 -> 12:00:00 PM
2.1 First calculation
This calculation returns the total overlapping time for the first date. The MEDIAN function lets you calculate overlapping time between two different date and/or time ranges. The MOD function removes the integer part of a number if the second argument is 1. The overlapping time for the start date/time is between 9:15:16 AM and 12:27:13 PM which is 3:11:57 meaning 3 hours, 11 minutes and 57 seconds. Excel uses decimal numbers
- MEDIAN(C5,C6,1)-MEDIAN(C5,C6,MOD(C10,1))
C5 is the start of the time range. C6 is the end of the time range. C10 is the start of the date/time range. 1 represents 12:00 AM.
MEDIAN(C5,C6,1) returns 0.518900462962963 which represents 12:27:13 AM.
MEDIAN(C5,C6,MOD(C10,1)) returns 0.38560185184906 which represents 9:15:16 AM.
0.518900462962963 - 0.38560185184906 equals 0.133298611 which is 3:11:57
The first day 1/7/2028 has 3 hours 11 minutes and 57 seconds overlapping.
2.2 Second calculation
This calculation returns the total overlapping time for the last date. The overlapping time for the end date/time is between 7:42:49 AM and 12:27:13 PM which is 0 (zero). They don't overlap.
2.3 Third calculation
The last calculation adds the time for days between the start and end date/time excluding the start and end date/time.
- (INT(C11)-(INT(C10)+1))*(C6-C5)
Dates are integers in Excel. There are 5 days between 1/7/2028 and 1/13/2028 if we exclude the start and end dates, they are: 1/8/2028, 1/9/2028, 1/10/2028, 1/11/2028 and 1/12/2028.
The time range for each day is 12:27:13 PM - 8:15:00 AM equals 3 hours, 11 minutes, and 57 seconds. The calculation in Excel is 0.518900462962963-0.34375 equals 0.175150462962963 which is 3 hours, 11 minutes, and 57 seconds.
5*0.175150462962963 = 0.875752314814815 which is 21 hours, 1 minute, and 5 seconds.
2.4 Calculating the total
The times from each calculation above are:
- 3 hours 11 minutes and 57 seconds or 0.133298611.
- 0 (zero) from the second calculation.
- 21 hours, 1 minute, and 5 seconds or 0.875752314814815 from the third calculation.
The total becomes 24 hours, 13 minutes, and 2 seconds or 1.00905092592872.
These articles are related:
- How to sum overlapping time based on minutes
- How to calculate overlapping time ranges
- Units contained in a range that overlap another range
3. Calculate total time based on different weekday time ranges overlapping multiple days
Question:
I need to calculate how many hours a machine is utilized in a company with a night and day shift?
The day shift hours:
Mon: 06:15 AM - 3:15 PM
Tue: 06:15 AM - 3:15 PM
We: 06:15 AM - 3:15 PM
Thu: 06:15 AM - 3:15 PM
Fri: 06:15 AM - 11:15 AM
Sat:
Sun:
The night shift hours:
Mon: 8:00 PM - 12:00 AM
Tue: 8:00 PM - 12:00 AM
We: 8:00 PM - 12:00 AM
Thu: 9:00 PM - 12:00 AM
Fri: 12:00 AM - 2:45 AM
Sat:
Sun:
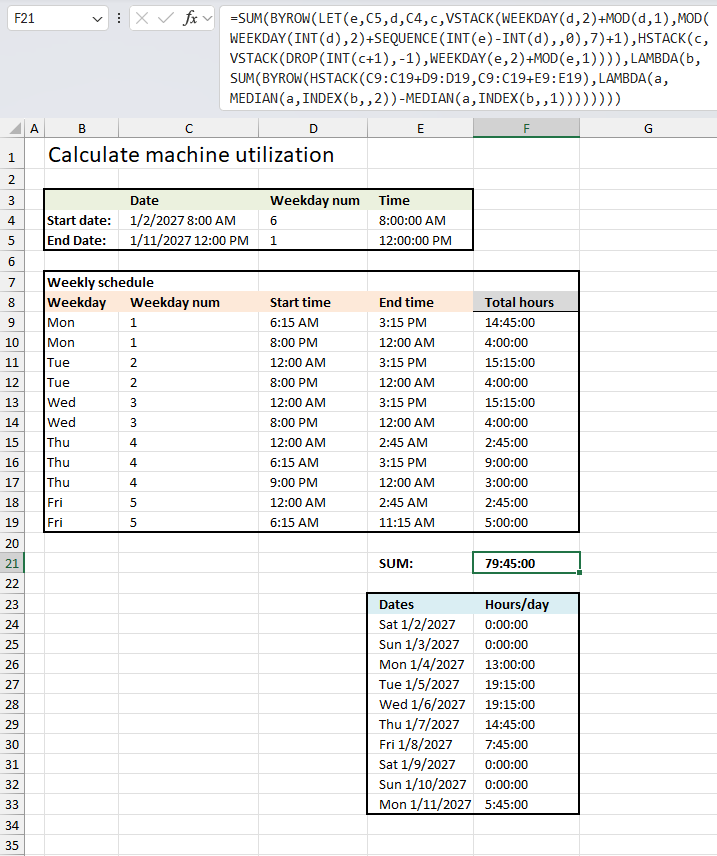
Machine utilization date and time range
Start date and time: 1/2/2027 08:00 AM
End date and time: 1/11/2027 12:00 PM

The image above shows the start date and time value in cell C4 and end date and time value in cell C5. This date and time range will overlap the day and night shift hours, some times overlap multiple times.
| Date | Weekday number | Time | |
| Start date: | 1/2/2027 8:00 AM | 6 | 8:00:00 AM |
| End Date: | 1/11/2027 12:00 PM | 1 | 12:00:00 PM |
Cell B9 to E19 contains the day and night shift hours specified per weekday. This example shows a week starting with Monday to Sunday with corresponding weekday numbers in cells B9 to B19. These numbers are important, they allow for calculating time total based on an overlapping day and night shift schedule.
| Weekday | Weekday number | Start time | End time |
| Mon | 1 | 6:15 AM | 3:15 PM |
| Mon | 1 | 8:00 PM | 12:00 AM |
| Tue | 2 | 12:00 AM | 3:15 PM |
| Tue | 2 | 8:00 PM | 12:00 AM |
| Wed | 3 | 12:00 AM | 3:15 PM |
| Wed | 3 | 8:00 PM | 12:00 AM |
| Thu | 4 | 12:00 AM | 2:45 AM |
| Thu | 4 | 6:15 AM | 3:15 PM |
| Thu | 4 | 9:00 PM | 12:00 AM |
| Fri | 5 | 12:00 AM | 2:45 AM |
| Fri | 5 | 6:15 AM | 11:15 AM |
Formula in cell F21:
Date and time range 1/2/2027 8:00 AM - 1/11/2027 12:00 PM overlaps these day and night shift ranges:
| Weekday | Weekday num | Start time | End time | Total hours |
| Mon | 1 | 6:15 AM | 3:15 PM | 14:45:00 |
| Mon | 1 | 8:00 PM | 12:00 AM | 4:00:00 |
| Tue | 2 | 12:00 AM | 3:15 PM | 15:15:00 |
| Tue | 2 | 8:00 PM | 12:00 AM | 4:00:00 |
| Wed | 3 | 12:00 AM | 3:15 PM | 15:15:00 |
| Wed | 3 | 8:00 PM | 12:00 AM | 4:00:00 |
| Thu | 4 | 12:00 AM | 2:45 AM | 2:45:00 |
| Thu | 4 | 6:15 AM | 3:15 PM | 9:00:00 |
| Thu | 4 | 9:00 PM | 12:00 AM | 3:00:00 |
| Fri | 5 | 12:00 AM | 2:45 AM | 2:45:00 |
| Fri | 5 | 6:15 AM | 11:15 AM | 5:00:00 |
The right-most column in the table above contains the total time per each day and night shift schedule in a week. The following formula creates this dynamic array shown in cell range F9:F19.
Formula in cell F9:
This formula in cell F9 is similar to the formula in cell F24, the difference is that the formula breaks down the hours per each day in the given date and time range specified in cells C4 and C5. The formula in cell F9 breaks down the total per schedule row given in cell range B9:F19.
The formula in cell F24 is the same as in cell F21 with one exception, the SUM function is removed. This creates a dynamic array that spills to cells below automatically as far as needed. If you change the date and time range in cells C4 and C5 the formula automatically adjusts the output. This is great for a breakdown of the hours for each day in the given date and time range.
This example shows a date and time range that overlaps Mondays twice which creates a larger total for that day than the specified time range. For example, 3:15 PM - 6:15 AM is 9:00 hours but the total is 14:45:00 for the first row in the day and night schedule. This is explained by the date and time range overlapping this time range twice making the total larger than the given time range.
If you add the time intervals in cell range F9:F19 you will get 79:45 hours, you will get the same result if you add the time intervals in cells F24:F33.
Explaining the formula
The MEDIAN function allows you to calculate the overlapping time range based on two date and time ranges.
MEDIAN(Start1,End1,End2) - MEDIAN(Start1,End1,Start2)
- Start1 is the starting point for date and time range 1
- End1 is the ending point for date and time range 1
- Start2 is the starting point for date and time range 2
- End2 is the ending point for date and time range 2
The MEDIAN function is not capable of calculating a result based on an array of intervals, that is until now. The new Excel 365 BYROW function changes this, it is now possible to calculate overlapping date ranges across multiple intervals.
By employing two distinct BYROW functions, we can achieve the following:
- Iterate through all days within the specified date and time range.
- Iterate through each row in the day and night schedule.
This allows us to calculate both the total and a detailed breakdown of the total across all days in the given date and time range. Furthermore, it also enables the calculation of a breakdown of the total per row in the day and night schedule.
The array that displays the detailed breakdown of the total across days indicates no values for both Saturday and Sunday. This is accurate because the schedule does not contain any intervals for those particular weekdays.
The total in cell F21 has the following formatting applied: [h]:mm:ss This allows hours being greater than 24 which is the number of hours in one day. This format is useful for displaying long durations larger than 24 hours.
The WEEKDAY function enables us to calculate numbers representing the weekday starting from 1 (Monday) to 7 (Sunday) for each day in the date and time interval. This makes the data coherent to the day and night schedule that is based on weekday numbers. The MEDIAN function can use these values to calculate a time value that represents overlapping interval.
Get Excel *.xlsx file
Dates category
Question: I am trying to create an excel spreadsheet that has a date range. Example: Cell A1 1/4/2009-1/10/2009 Cell B1 […]
This article demonstrates how to return the latest date based on a condition using formulas or a Pivot Table. The […]
This article explains how to search for a specific date and identify a date range in which it falls between […]
Excel categories
One Response to “Calculate machine utilization”
Leave a Reply
How to comment
How to add a formula to your comment
<code>Insert your formula here.</code>
Convert less than and larger than signs
Use html character entities instead of less than and larger than signs.
< becomes < and > becomes >
How to add VBA code to your comment
[vb 1="vbnet" language=","]
Put your VBA code here.
[/vb]
How to add a picture to your comment:
Upload picture to postimage.org or imgur
Paste image link to your comment.
Hi
Seek your help in resolving my problem. i need to calculate the m/c engagement time using simple Excel sheet where i enter the m/c start time in Cell B3 and the end time C3 we need the m/c engaged time in D3.
We are Job order company.We operate in Two shifts. Depending upon the load we will plan the machines.
A shifts starts by 9.00 and Ends by 18.00 ; Tea break is from 10.30 to 10.45 and 15.00 to 15.15; Lunch is from 13.00 to 13.30. Similarly B shifts starts by 18.00 and Ends by 3.00 in next morning ; Tea break is from 19.00 to 19.15 and 00.15 to 00.30; Dinner is from 22.00 to 22.30. Please help me.
Regards
Sivakumar MP